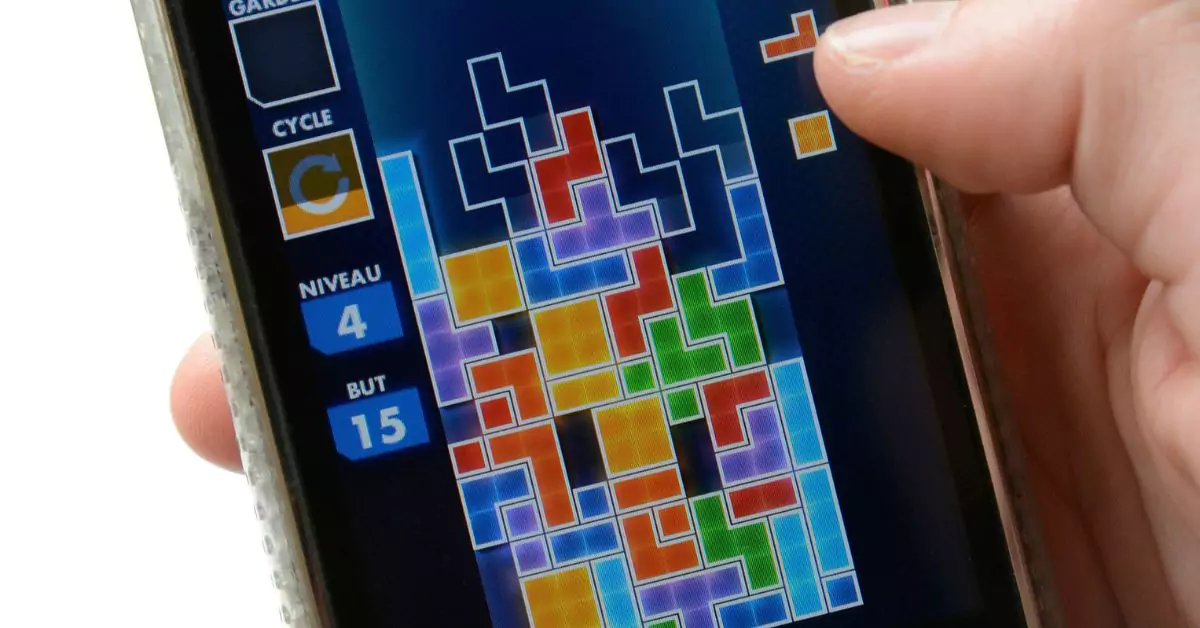
Remember the good old days when we used to huddle around old TVs, our eyes fixated on the colorful, geometric shapes cascading down the screen? Yes, we’re talking about Tetris – the quintessential puzzle game that became a staple in our childhoods. But little did we know, as we expertly rotated and arranged those blocks, that Tetris would transcend its status as a mere pastime. Today, it’s emerging as a beacon of hope in the field of mental health.
In a remarkable turn of events, a study published in the esteemed Journal of Psychiatry & Neuroscience has shed light on an unexpected facet of this beloved game. It turns out, playing Tetris might be more than just entertaining; it could be a powerful tool in combating post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). This groundbreaking research, emerging from the heart of Berlin, suggests that our old-school game could have a profound impact on one of the most challenging mental health conditions.
In this article, we’ll dive into the details of this fascinating study and explore how Tetris, a game we all know and love, is making waves in the world of therapeutic interventions. Join us as we unpack the potential of Tetris in providing relief to those battling PTSD, making our journey down memory lane not just nostalgic, but also surprisingly enlightening.
A Brief History of Tetris
Tetris, a name synonymous with gaming history, began its journey in 1984, birthed in the Cold War era’s Soviet Union. Created by Alexey Pajitnov, a software engineer, the game’s simple yet captivating concept quickly caught the world’s attention. It’s a tale of blocks, known as Tetriminos, falling into a matrix, where players aim to create complete lines that then disappear, preventing the stack from reaching the top of the screen.
Crossing Borders and Breaking Records
What started as a basic computer program soon crossed borders, captivating players worldwide. By the late 1980s, Tetris had become a global phenomenon, finding its way onto virtually every gaming platform available. Its appeal lay in its simplicity and the universal challenge it presented, making it a game for all ages and backgrounds. It wasn’t just a game; it became a cultural icon, inspiring everything from fashion to art, and even academic studies.
Transition to a Therapeutic Tool
While most recognized Tetris for its entertainment value, few could have predicted its potential impact on mental health. The game’s repetitive and engaging nature, requiring focus and spatial awareness, hinted at benefits beyond mere leisure. This transition from a global gaming sensation to a potential therapeutic tool marks a significant shift in how we perceive video games and their impact on mental health.
Understanding PTSD
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition triggered by experiencing or witnessing a terrifying event. Symptoms may include flashbacks, nightmares, severe anxiety, and uncontrollable thoughts about the event. It can significantly impact a person’s daily life and well-being, making coping with normal activities a challenge.
Common Symptoms and Traditional Treatments
Those living with PTSD often struggle with intrusive memories, emotional numbness, and heightened alertness. Traditional treatments include psychotherapy, such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), and medications like antidepressants. However, not everyone responds well to these treatments, highlighting the need for alternative approaches.
The Psychological Impact
PTSD is more than just a collection of symptoms; it’s a condition that can profoundly affect a person’s life. Relationships, work, and the ability to enjoy life can all be severely impacted. Understanding PTSD is crucial in appreciating the significance of new and innovative treatments, such as the role Tetris might play in alleviating these symptoms.
The Berlin Study: Overview and Methodology
The recent study conducted in Berlin, Germany, and published in the Journal of Psychiatry & Neuroscience, represents a significant advancement in PTSD research. This study is notable not just for its intriguing subject – the use of Tetris – but also for its meticulous methodology and the prestige of the publishing journal.
Research Team and Study Significance
Conducted by a dedicated team of researchers, the study aimed to explore unconventional methods in treating PTSD. The choice of Tetris, a game known for its simplicity and cognitive engagement, was a deliberate one, aimed at understanding how certain types of cognitive activities can influence PTSD symptoms.
Methodology: Participants and Procedure
The study included 40 men, all with combat-related PTSD from the German Federal Armed Forces. They were randomly assigned to two groups: one that played Tetris and a control group that did not. The Tetris group engaged in playing the game for 60 minutes daily for about six weeks. In addition to this, participants from both groups underwent EMDR therapy, a common treatment for PTSD.
Key Findings of the Study
The results of the Berlin study were eye-opening. Participants in the Tetris group showed remarkable improvements in various PTSD symptoms. Notably, there was a significant reduction in intrusive memories, nightmares, and avoidance behavior. This was in stark contrast to the control group, which did not exhibit the same level of improvement.
Comparison with the Control Group
The control group, which did not engage in playing Tetris, provided a critical baseline for evaluating the game’s effectiveness. While both groups underwent EMDR therapy, the addition of Tetris to the treatment regime appeared to accelerate and enhance recovery from PTSD symptoms in the experimental group.
Sustained Benefits Over Time
Perhaps one of the most promising aspects of the study was the longevity of its effects. The improvements in PTSD symptoms were not just immediate but also sustained. Participants were followed up six months after the study, and the benefits gained from playing Tetris were largely maintained, suggesting a lasting impact.
How Does Tetris Help with PTSD?
One of the core benefits identified in the study is Tetris’s ability to reduce the frequency and intensity of intrusive memories, a common and distressing symptom of PTSD. This is believed to be due to the game’s requirement for visual-spatial skills, which helps distract the mind and redirect attention away from traumatic memories.
Improvement in Cognitive Function
PTSD is often associated with changes in brain structure and function, particularly in areas related to memory and stress response, like the hippocampus. Playing Tetris, with its cognitive demands, may stimulate the brain in a way that helps improve cognitive function and potentially increases hippocampal volume, as seen in other cognitive training studies.
Psychological Mechanisms at Play
The psychological mechanisms underlying the effectiveness of Tetris in treating PTSD symptoms are multifaceted. By providing a structured, predictable, and controllable environment, Tetris may offer a sense of order and control that is often lacking in the lives of those with PTSD. This, combined with the cognitive challenge and distraction it provides, makes it a unique tool in managing PTSD symptoms.
Implications and Future Directions
The study’s findings open the door to viewing video games like Tetris as potential therapeutic tools. This represents a significant shift in the approach to treating PTSD, broadening the scope of interventions available to those suffering from this condition.
Need for Further Research
While the results are promising, the study’s authors emphasize the need for further research. This includes exploring the optimal duration and intensity of Tetris play, understanding its effects on different PTSD populations, and investigating how it can be best integrated into existing treatment protocols.
Broader Impact on Mental Health Treatment
The use of Tetris in PTSD treatment points to a larger trend of integrating digital and interactive tools into mental health care. This innovative approach could reshape how we think about and address various mental health conditions, making treatment more accessible and engaging for patients.
Conclusion
The journey from a beloved childhood game to a potential therapeutic intervention is nothing short of remarkable. Tetris, a game that once captivated our attention on old TVs, now holds the potential to change lives by alleviating the symptoms of PTSD. While further research is needed, the implications of this study are far-reaching, offering new hope and possibilities in the treatment of PTSD and mental health more broadly.
If you or someone you know is struggling with PTSD, it’s essential to consult with healthcare professionals to explore all treatment options. As we continue to discover and understand the therapeutic benefits of games like Tetris, the future of mental health treatment looks more diverse and promising.