Explore the top 10 foods that can slow down your metabolism and contribute to weight gain. From soda to ‘diet’ foods, learn how these common items impact your body and discover healthier alternatives. Boost your metabolism with our comprehensive guide to making smarter food choices. Perfect for anyone looking to improve their diet and understand the effects of what they eat on their body’s metabolic rate.
Welcome to our in-depth exploration of how everyday foods can impact your metabolism and overall health. In this guide, we uncover the truth behind ten common foods and ingredients that might be secretly slowing down your metabolism, leading to unwanted weight gain and affecting your overall well-being. From the deceptive sweetness of soda to the hidden pitfalls of “diet” foods, we delve into how these items can disrupt your body’s natural processes.
Alongside this, we provide healthier alternatives and practical tips to help you make better dietary choices. Whether you’re aiming to lose weight, maintain a healthy lifestyle, or simply curious about the effects of your diet on your metabolism, this guide offers valuable insights and advice to empower your nutritional decisions. Join us as we navigate the complex world of food and metabolism, transforming knowledge into action for a healthier you.
Soda:
Sodas are not only high in high-fructose corn syrup, which is more harmful than regular sugar, but they also contain caffeine and artificial additives that can disrupt your metabolism. The lack of nutritional value and the presence of phosphoric acid can also lead to bone weakening. Regular consumption can lead to insulin resistance, a precursor to diabetes.
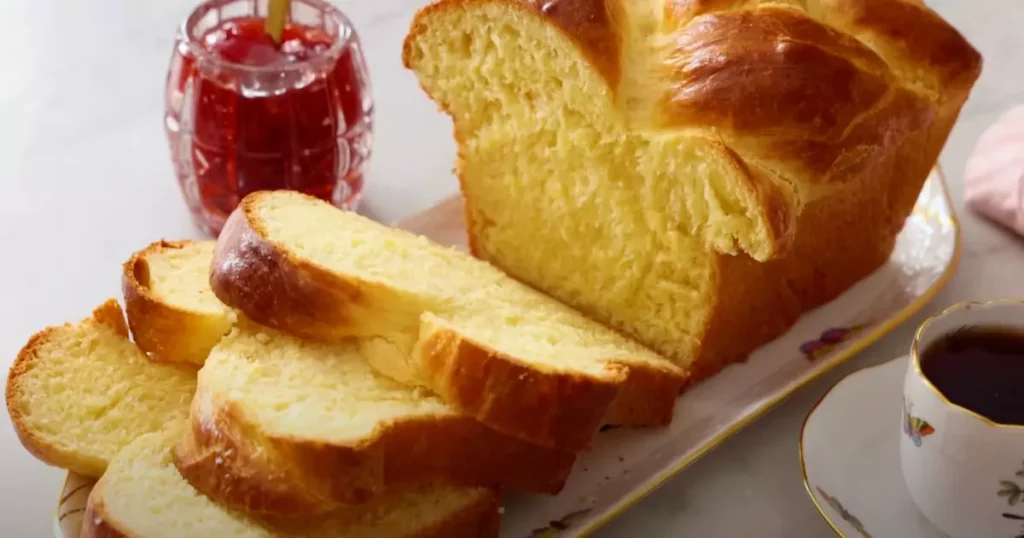
White Bread:
Made from heavily processed white flour, white bread lacks the bran and germ that give whole grains their nutritional value. This leads to a rapid spike in blood sugar and insulin levels, contributing to fat storage and an increased appetite. It’s also often high in added sugars and preservatives.
Conventionally-Farmed Beef:
The antibiotics used in conventionally farmed beef can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria, essential for a healthy metabolism. This meat is also often higher in unhealthy saturated fats compared to grass-fed beef, which can contribute to heart disease and other health issues.
Fruit Juices:
Many commercial fruit juices are essentially sugary beverages with little to no real fruit content. They lack the fiber of whole fruits, which is essential for maintaining a healthy digestive system and metabolism. Plus, the added sugars can contribute to liver overload and increased fat storage.
White Flour:
Products made from white flour, such as pastries, cookies, and certain pastas, rapidly convert to sugar in your bloodstream. This not only causes weight gain but also can lead to energy crashes and cravings, making it harder to maintain a healthy diet.
White Rice:
While a staple in many diets, white rice has a high glycemic index and can cause blood sugar levels to spike. It’s also less satisfying than whole grains, leading to overeating. Brown rice, quinoa, or other whole grains are healthier options that help maintain energy levels and metabolic rate.
Processed Vegetable Oil:
These oils, found in many processed and fried foods, contribute to inflammation and oxidative stress in the body. They can alter the balance of omega-3 to omega-6 fatty acids in the body, leading to various metabolic issues and increased risk of chronic diseases.
Artificial Sweeteners:
Regular consumption of artificial sweeteners can disrupt the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels, leading to metabolic confusion and an increased preference for sweet tastes. This can make it harder to control your diet and maintain a healthy weight.
Corn:
Besides being high glycemic, corn is often genetically modified and may contain residues of pesticides and herbicides, which can have additional negative health effects. Its consumption can lead to blood sugar imbalances and contribute to inflammation in the body.
“Diet” Foods:
These products often contain a range of artificial ingredients and fillers designed to reduce calories but can disrupt hormones and metabolism. They may also lead to a false sense of security, causing people to eat more or make poor dietary choices elsewhere.
Wrapping up our discussion on foods that can slow down your metabolism, it’s clear that our dietary choices have a profound impact on our body’s ability to process and utilize energy efficiently. This guide has highlighted the importance of being mindful of what we consume, particularly when it comes to items like soda, white bread, and artificially sweetened products.
By prioritizing whole, nutrient-rich foods and steering clear of those with empty calories and harmful additives, we can significantly enhance our metabolic health. Alongside a balanced diet, incorporating regular physical activity, staying hydrated, and getting enough rest are essential for optimal metabolic function. With these insights and adjustments to your eating habits, you’re on a path to not only improving your metabolism but also enhancing your overall health and quality of life. Here’s to making healthier choices and enjoying the benefits of a well-nourished, active body!