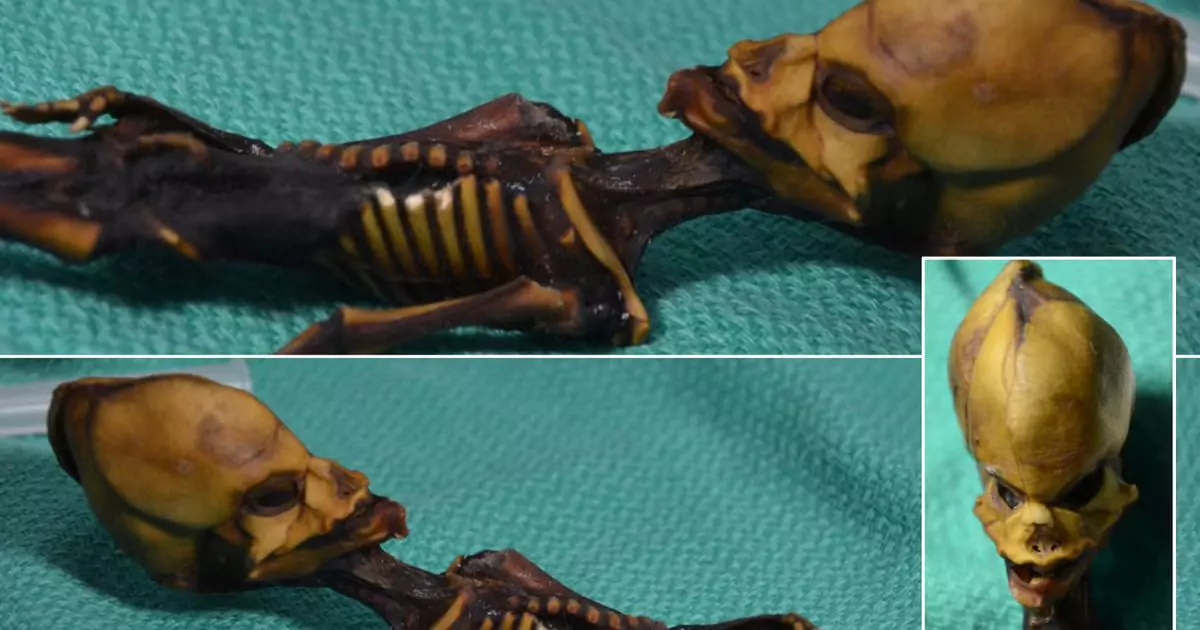
When a tiny mummified body was discovered in the Atacama Desert of Chile in 2003, it captured global attention and sparked widespread speculation. Nicknamed ‘Ata‘, the six-inch-long skeleton’s unusual appearance led many to theorize that it was of extraterrestrial origin. However, comprehensive genetic testing and analysis have solved the mystery, revealing a human story that underscores the importance of prenatal care and awareness of environmental health risks.
The Enigmatic Discovery That Stirred the World
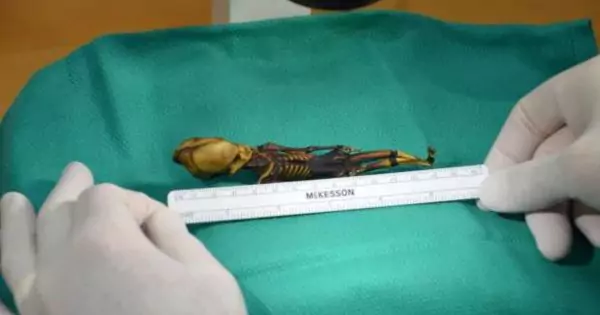
The mummified remains exhibited features that deviated significantly from typical human anatomy. With an elongated skull, slanted eye sockets, and only ten pairs of ribs instead of the usual twelve, Ata resembled depictions of aliens often portrayed in science fiction. These anomalies fueled conspiracy theories and captivated the internet. Many believed the specimen was evidence of alien life.
Speculations and Theories
People speculated extensively about Ata’s origins. Some thought it was an alien due to its size and shape. Others suggested it might be an ancient mummified human or even a fetus. The mystery deepened when tests indicated that Ata was about 40 years old at the time of death, ruling out the fetus theory.
Genetic Analysis Provides Definitive Answers
In 2018, a team of scientists led by Dr. Garry Nolan, a professor of microbiology and immunology at Stanford University, conducted extensive genetic analysis of Ata’s DNA. Collaborating with Atul Butte, director of the Institute for Computational Health Sciences at the University of California-San Francisco, they utilized advanced genome sequencing technologies.
Their research, published in the journal Genome Research, concluded that Ata was indeed a human female of Chilean descent. The DNA matched that of the local population, dispelling notions of extraterrestrial origin. Moreover, analysis of bone development indicated that she was likely stillborn or died shortly after birth. This finding contradicted earlier speculations that the remains were those of a six to eight-year-old child due to the apparent bone maturity.
Unraveling the Medical Mysteries
The scientists identified multiple genetic mutations associated with dwarfism, skeletal dysplasia, and other bone development disorders. Ata’s condition resulted from a combination of rare genetic defects that severely affected her physical development. The mutations impacted genes involved in bone formation and growth, leading to her unusual skeletal structure.
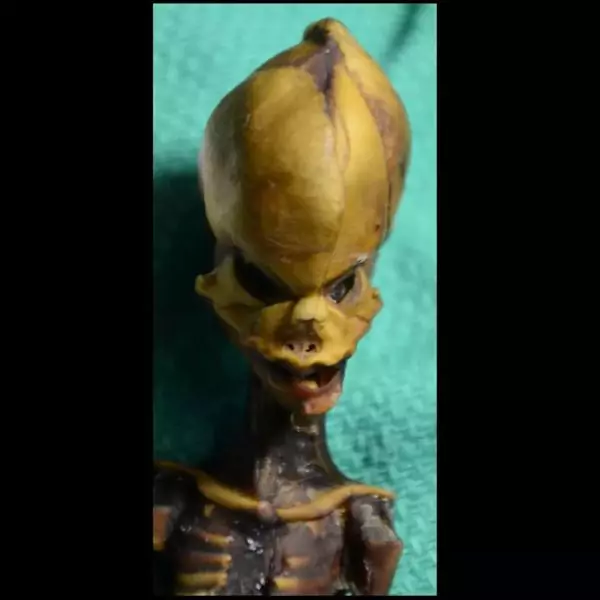
Dr. Nolan stated, “We found mutations in genes that are known to cause skeletal malformations. Some of the mutations are in genes that have never been associated with these conditions before.” This discovery contributes valuable insights to medical research, potentially aiding in the diagnosis and treatment of rare genetic disorders.
The Role of Environmental Factors
While genetics played a crucial role, researchers also considered environmental influences. Ata was found in La Noria, an abandoned mining town in the Atacama Desert. The area’s history of nitrate mining raises concerns about exposure to environmental toxins. Prenatal exposure to harmful substances can lead to DNA damage, increasing the risk of congenital anomalies.
Dr. Nolan suggested, “The specimen was found in La Noria, one of the Atacama Desert’s many abandoned nitrate mining towns. This suggests a possible role for prenatal nitrate exposure leading to DNA damage.” This highlights the importance of environmental health and the need for regulations to protect communities from hazardous exposures.
Ethical Considerations and Respect for Human Remains
The case of Ata also brings forth ethical considerations regarding the handling of human remains. It underscores the importance of respecting cultural heritage and adhering to ethical guidelines in archaeological research. The initial acquisition and subsequent studies of Ata’s remains raise questions about consent and the treatment of ancestral remains.
Precautions and the Importance of Prenatal Care
This discovery emphasizes several key precautions and considerations:
- Importance of Prenatal Care: Regular medical check-ups during pregnancy are crucial. Early detection of potential health issues can lead to interventions that improve outcomes.
- Environmental Health Awareness: Communities should be aware of environmental hazards, such as exposure to industrial pollutants. Advocacy for clean environments is essential for public health.
- Genetic Counseling and Testing: For those with a family history of genetic disorders, consulting with healthcare professionals about genetic counseling can provide valuable information and guidance.
- Ethical Research Practices: Scientists and researchers must follow ethical standards, especially when dealing with human remains, to respect cultural and individual rights.
- Supporting Medical Research: Continued support for medical and genetic research can lead to breakthroughs in understanding and treating rare conditions. Contributions to legitimate research organizations can make a significant impact.
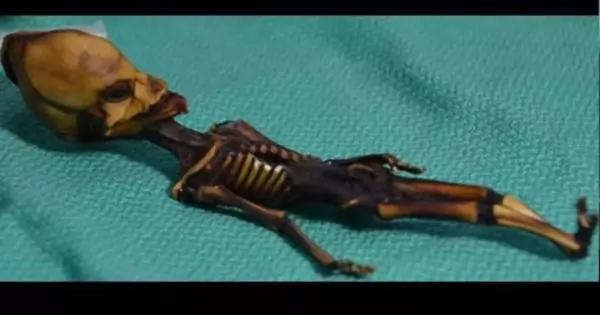
The Broader Impact on Medical Science
The genetic mutations identified in Ata open new avenues for research into skeletal abnormalities and other congenital disorders. By understanding these rare mutations, scientists can develop better diagnostic tools and potential therapies. This case reinforces the importance of advanced medical research and the role of genomics in uncovering the complexities of human development.
Future Implications
This research may help prevent or treat similar conditions in the future. It also emphasizes the need for environmental regulations to prevent exposure to harmful substances that can cause genetic mutations.
A Human Story Grounded in Science
The mystery of the so-called ‘Atacama Alien’ has been solved, not through speculation but through rigorous scientific inquiry. Ata was a human child with multiple genetic mutations that led to profound physical anomalies. Her story is a poignant reminder of the challenges that can arise from genetic disorders and environmental factors.
By approaching such mysteries with a commitment to science and ethics, we not only uncover the truth but also contribute to knowledge that can benefit humanity. The advancements in genetic analysis and the lessons learned from Ata’s case highlight the interconnectedness of medical science, ethical responsibility, and human compassion.