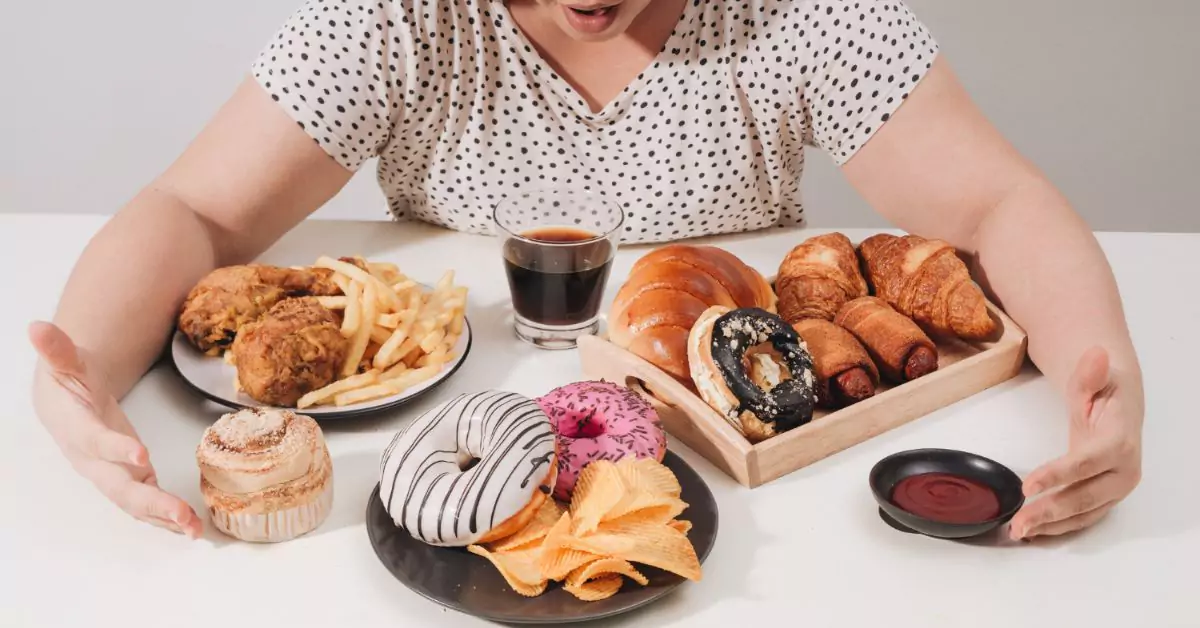
Did you know that the very first meal of your day could be silently sabotaging your gut health and contributing to weight gain? While breakfast is often celebrated as the most important meal of the day, not all breakfast foods are created equal. Some of the most common and beloved morning choices rank among the worst for our digestive system and weight management.
This revelation is crucial because what we consume in the morning can set the tone for our entire day’s nutrition and well-being. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the three worst breakfast foods, as identified by health experts, that could be wreaking havoc on your gut health and tipping the scales in the wrong direction.
Understanding these dietary pitfalls is essential, not only for those focusing on weight management but also for anyone aiming to maintain a healthy and balanced diet. By exploring the intricate connection between diet, gut health, and weight, this article will provide valuable insights into making smarter, gut-friendly breakfast choices.
The Importance of Gut Health and Weight Management
Overview of Gut Health
Gut health, a term that has gained significant attention in recent years, refers to the function and balance of bacteria in the many parts of the gastrointestinal tract. Ideally, organs like the esophagus, stomach, and intestines all work together to allow us to eat and digest food without discomfort.

But the core component of gut health is the gut microbiome – the vast ecosystem of organisms such as bacteria, yeasts, fungi, viruses, and protozoans that live in our digestive tract. These microscopic beings play a crucial role in digesting food, absorbing nutrients, and fortifying the body’s defense system.
A healthy gut microbiome is not only vital for physical health but also for mental well-being, with emerging research linking gut health to mood and mental health. Thus, maintaining a balanced gut microbiome is essential for overall health and well-being.
Relationship Between Diet, Gut Health, and Weight
The relationship between our diet, gut health, and weight is a complex and interwoven one. What we eat directly affects the composition of our gut microbiome. A diet high in diverse and nutritious foods promotes a diverse microbiome, which is beneficial for gut health and overall wellness.
On the other hand, a diet high in processed foods, added sugars, and unhealthy fats can lead to an imbalance in gut bacteria, known as dysbiosis. This imbalance can trigger inflammation, increase the risk of intestinal and metabolic disorders, and even affect mental health. Furthermore, the gut microbiome plays a pivotal role in weight management.
Certain gut bacteria types are known to influence how we store fat, how we balance levels of glucose in the blood, and how we respond to hormones that make us feel hungry or satiated. Thus, the right diet is not just about reducing calorie intake but also about nurturing the gut microbiome, which in turn can aid in weight management and overall health.
The Three Worst Breakfast Foods
1. Pastries
Pastries and Gut Health
Pastries, a common breakfast choice for many due to their convenience and taste, are actually one of the worst offenders for gut health. The primary issue lies in their core ingredients: refined flour and sugar. Refined flour, stripped of its natural fiber during processing, disrupts the balance of gut microbiota. A diet low in fiber fails to provide the necessary substrates for beneficial gut bacteria to thrive. This can lead to an overgrowth of harmful bacteria and a decrease in gut flora diversity, which is crucial for a healthy digestive system.
Moreover, the high sugar content in pastries poses another threat. Excessive sugar intake is known to feed certain types of bacteria and yeasts in the gut, like candida, which can overpower beneficial bacteria. This imbalance can lead to various gut health issues, including inflammation, increased gut permeability (often referred to as ‘leaky gut’), and even chronic diseases.

Sugar and Weight Gain
From a weight management perspective, the high sugar and refined carb content in pastries significantly contribute to weight gain. These ingredients cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels, leading to a surge in insulin, the hormone responsible for sugar regulation in the bloodstream. High insulin levels are associated with increased fat storage, especially around the abdomen. Furthermore, the quick digestion of these simple carbohydrates leaves you feeling hungry sooner, potentially leading to overeating. Regular consumption of sugary pastries can also lead to insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes and a factor in obesity.
2. Highly Processed Breakfast Meats
Processed Meats and Gut Inflammation
Highly processed breakfast meats like sausages and bacon are another group of foods detrimental to gut health. These meats typically contain high levels of saturated fats and additives, including preservatives like sodium nitrate. Saturated fats are known to induce gut inflammation and can alter the gut microbiota composition, promoting the growth of bacteria linked to inflammatory gut diseases.
The additives in processed meats also pose a concern. They can disrupt the gut barrier function and negatively impact gut bacteria. Regular consumption of these meats has been associated with an increased risk of colorectal cancer and other gastrointestinal disorders.

Breakfast Meats and Weight
Concerning weight management, processed breakfast meats contribute to weight gain due to their high fat and calorie content. The saturated fats in these meats are not only linked to increased body fat but also to insulin resistance. This can exacerbate the risk of developing metabolic disorders, including obesity and type 2 diabetes. Additionally, the high sodium content in processed meats can lead to water retention, giving a false sense of weight gain and bloating.
3. Cereals with Artificial Sweeteners
Artificial Sweeteners in Cereals
Many breakfast cereals, often marketed as healthy choices, contain artificial sweeteners that can be detrimental to gut health. These sweeteners, while low in calories, can disrupt the microbiome balance. They interfere with the growth and function of beneficial gut bacteria and may promote the growth of harmful bacteria, leading to dysbiosis.
Artificial sweeteners have also been linked to changes in the gut’s ability to metabolize nutrients and regulate blood sugar levels. This can affect overall gut health, leading to gastrointestinal symptoms like bloating, gas, and discomfort.

Cereals, Gut Health, and Obesity
In terms of weight management, the role of artificial sweeteners is complex and somewhat paradoxical. While they are used to reduce calorie intake, studies have suggested that they may actually contribute to weight gain. They can disrupt the body’s ability to regulate calorie intake and blood sugar levels, potentially leading to increased calorie consumption and cravings for sugary foods.
Moreover, artificial sweeteners may affect insulin response and glucose metabolism, factors closely linked to weight management. Regular consumption of cereals with artificial sweeteners can therefore contribute to weight gain and obesity, contrary to their intended purpose of weight management.
Healthier Breakfast Alternatives
When considering healthier alternatives for breakfast, the focus should be on nutrient-dense foods that promote gut health and aid in weight management. Opting for high-fiber, protein-rich foods can make a significant difference. These nutrients are essential for maintaining a healthy gut microbiome and keeping you satiated, which helps in controlling weight.

High-Fiber Foods: Fiber plays a pivotal role in gut health. It acts as a prebiotic, feeding the good bacteria in the gut. Foods like oatmeal, whole-grain bread, and fresh fruits are excellent sources of fiber. For example, starting your day with a bowl of oatmeal topped with berries and seeds can provide a fiber-rich, nutrient-packed breakfast.
Protein-Rich Foods: Incorporating protein into your breakfast can help in managing appetite and maintaining lean muscle mass, which is crucial for a healthy metabolism. Eggs, Greek yogurt, and lean meats like turkey or chicken are good sources of high-quality protein. A breakfast scramble with vegetables and eggs or a Greek yogurt parfait with nuts and fruit can be both satisfying and nutritious.
Combining Fiber and Protein: A balanced breakfast that includes both fiber and protein can keep you full longer and provide sustained energy. A smoothie with spinach, a scoop of protein powder, and a piece of fruit, or whole-grain toast with avocado and a poached egg, are examples of combining these nutrients effectively.
Keywords: “healthy breakfast,” “fiber-rich foods,” “protein in breakfast”
Expert Opinions and Studies
Health and nutrition experts emphasize the importance of choosing the right foods for breakfast. According to a study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, a high-fiber breakfast can significantly improve gut health by increasing beneficial bacterial diversity. Another study in the Journal of Nutrition suggests that a high-protein breakfast can aid in weight management by reducing cravings and calorie intake throughout the day.
These studies reinforce the idea that the composition of our first meal plays a crucial role in our overall health. By opting for fiber and protein-rich options, we can positively influence our gut microbiome and manage our weight more effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while certain popular breakfast foods like pastries, processed meats, and artificially sweetened cereals can negatively impact gut health and contribute to weight gain, there are healthier alternatives available. Opting for high-fiber and protein-rich foods can enhance gut health, aid in weight management, and provide sustained energy throughout the day. Making informed choices about our morning meals is a simple yet effective step towards better health and well-being.