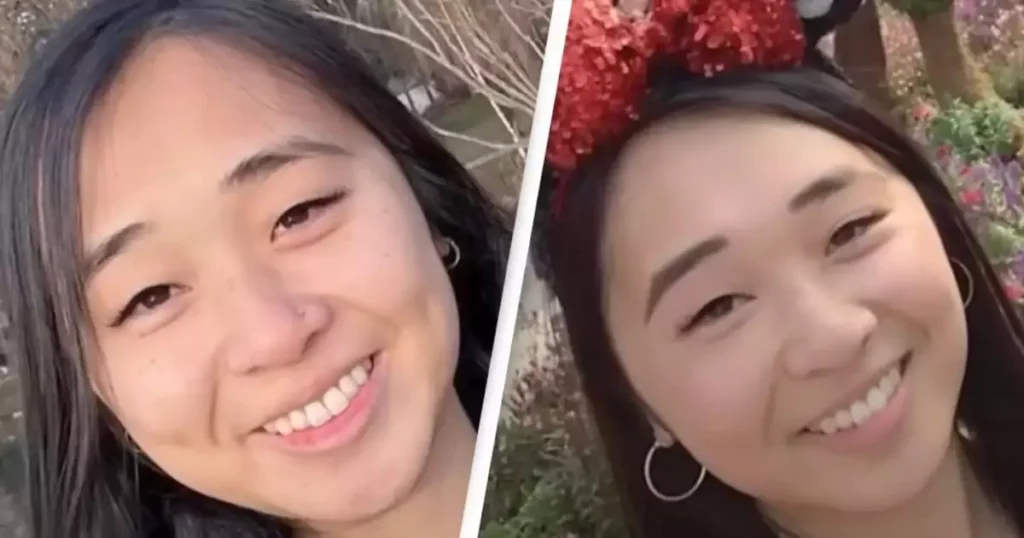
In the digital age, where technology continually reshapes our understanding of reality, “deepfakes” represent a significant milestone in the evolution of digital media. A deepfake is an advanced form of digital manipulation where artificial intelligence (AI) is used to create or alter video and audio content with a high degree of realism. This technology, leveraging deep learning and Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), can generate images, videos, or audio recordings that convincingly mimic real people, often to the point of being indistinguishable from genuine content. The term itself is a blend of “deep learning” and “fake,” succinctly encapsulating its nature.
The emergence of deepfakes has profound implications. It redefines the boundaries between truth and fiction in digital media, posing new challenges in areas ranging from personal security to political discourse. In a world increasingly reliant on digital communication, understanding deepfakes – their creation, identification, and impact – becomes crucial for navigating the complexities of the information age.

What are Deepfakes?
Deepfakes are synthetically created or altered media in which a person’s likeness – their face, voice, or both – is replaced with someone else’s likeness, using AI algorithms. This technology creates hyper-realistic results, making it difficult to distinguish between authentic and altered media.
History and Evolution: The concept of manipulating media is not new, but the use of AI to do so is a recent development. Deepfake technology has evolved rapidly, largely due to advancements in AI and machine learning. Initially a tool of researchers and hobbyists, it has now gained widespread attention for its potential and risks.
Difference from Traditional Media Manipulation: Unlike traditional methods, such as photo editing software that requires manual input, deepfakes rely on AI to automate and refine the manipulation process. This AI-driven approach allows for more realistic and convincing alterations, often requiring less technical expertise from the user.
How Deepfakes Work
Combination of Algorithms: Deepfakes utilize two types of algorithms: generators and discriminators. The generator creates the fake image or video, while the discriminator evaluates its authenticity. The continuous interaction between these algorithms under the GAN framework improves the quality of the output.
Deep Learning in Deepfakes: Deep learning algorithms analyze vast amounts of data – images, videos, and voice recordings – to understand and replicate the nuances of human expressions and speech. This learning process enables the creation of highly realistic deepfake content.

Role of GANs: GANs are critical in refining deepfake technology. They consist of two neural networks – the generator and the discriminator – that work against each other, hence ‘adversarial.’ The result is a more sophisticated and believable deepfake.
Real-world Applications: While controversial, deepfakes have potential applications in various fields, including entertainment, where they can be used for realistic special effects, and education, where they can bring historical figures to life in interactive learning environments.
An intriguing example is the trailer of “Home Alone 3,” which showcases the capabilities of deepfake technology in reimagining cinematic experiences. Viewers are invited to check out this trailer to see firsthand how deepfake technology can transform familiar content into something entirely new and unexpected.
The Potential and Perils of Deepfakes
Positive Applications: In entertainment, deepfakes can revolutionize storytelling by allowing filmmakers to create scenes with deceased actors or younger versions of living actors. In education, they offer immersive learning experiences, and in art, they open new avenues for creative expression.
Risks and Dangers: The primary concern with deepfakes is their potential for misuse. They can be used to spread misinformation, commit identity theft, and create non-consensual content, undermining trust in digital media and posing significant ethical and legal challenges.
How to Spot a Deepfake
Detection Guide: Identifying deepfakes involves looking for anomalies like unnatural eye movement or facial expressions, inconsistencies in body movements, odd skin tones or lighting, and discrepancies in audio and video synchronization. These signs can help distinguish deepfakes from genuine content.
Audio-Visual Inconsistencies: Deepfakes often struggle to perfectly align audio with corresponding visual movements, particularly in speech and facial expressions. Observing these mismatches can be key to detection.
Case Studies: Examining real-life instances of identified deepfakes can provide valuable insights into their detection and the evolving techniques used to create them.
Technological Advances in Deepfake Detection
Blockchain and Cryptography: Blockchain technology and cryptographic algorithms are emerging as potent tools in verifying the authenticity of digital content. By creating a digital fingerprint or cryptographic hash for genuine videos at the time of creation, it becomes easier to identify tampered content. Blockchain’s immutable nature ensures that once a video is recorded on the ledger, its authenticity can be verified, making it harder for deepfakes to pass as original.
Overview of Detection Tools: The battle against deepfakes has spurred the development of sophisticated detection tools. These tools analyze videos and images for inconsistencies typically missed by the human eye. They use machine learning algorithms to identify signs of manipulation, such as unnatural facial movements or discrepancies in lighting and shadows.
5 Best Deepfake Detector Tools
1. Sentinel: AI-Based Deepfake Detection
Sentinel stands out as a premier AI-based platform designed to combat deepfake threats. Utilized by democratic governments, defense agencies, and enterprises across Europe, Sentinel’s technology is pivotal in preserving the integrity of digital media. The system allows users to upload media via a website or API, where it undergoes AI-forgery analysis. It provides detailed feedback, including a visualization of the manipulated areas, allowing users to see the specific alterations made.
Key Features of Sentinel:
- Advanced AI algorithms for deepfake detection.
- Visualization of manipulated media segments.
- Wide usage across European organizations.
2. Intel’s Real-Time Deepfake Detector: FakeCatcher
Intel’s FakeCatcher is a groundbreaking real-time deepfake detector, boasting a remarkable 96% accuracy rate. Developed in collaboration with the State University of New York at Binghamton, this technology harnesses Intel hardware and software for rapid analysis. FakeCatcher uniquely identifies deepfakes by analyzing subtle “blood flow” signals in video pixels, a characteristic feature of authentic human videos, offering instant verification.
Key Features of Intel’s FakeCatcher:
- 96% accuracy rate in deepfake detection.
- Real-time analysis capabilities.
- Unique blood flow signal analysis for authenticity checks.
3. WeVerify: Human-in-the-Loop Verification
WeVerify focuses on developing smart verification tools for content and disinformation analysis. The project emphasizes cross-modal content verification and social network analysis to identify and debunk fabricated content. Its approach includes a blockchain-based public database, cataloging known fakes and providing an ecosystem for reliable content verification.
Key Features of WeVerify:
- Human-in-the-loop content verification methods.
- Blockchain-based database of known fakes.
- Comprehensive social media and web content analysis tools.
4. Microsoft’s Video Authenticator Tool
Microsoft’s Video Authenticator Tool is a sophisticated solution for analyzing photos or videos to detect deepfakes. It provides a real-time confidence score, indicating the likelihood of media manipulation. The tool excels in identifying subtle changes in grayscale elements, a common indicator of deepfakes, and is particularly useful for instant verification needs.
Key Features of Microsoft’s Video Authenticator Tool:
- Real-time analysis with confidence scoring.
- Detection of subtle grayscale alterations indicative of deepfakes.
- Suitable for both still photos and video content.
5. Deepfake Detection Using Phoneme-Viseme Mismatches
Developed by researchers at Stanford University and the University of California, this technique targets the inconsistencies between visemes (mouth shapes) and phonemes (spoken words) in deepfakes. Since AI often struggles to align mouth movements with spoken words accurately, this method effectively identifies deepfakes by spotting such mismatches.
Key Features of Phoneme-Viseme Mismatch Detection:
- Focus on mismatches between visemes and phonemes.
- Advanced AI algorithms for detailed analysis.
- Strong indication of deepfakes upon detecting mismatches.
The Social and Legal Impact of Deepfakes
Social and Political Impact: Deepfakes pose significant challenges to society and politics by enabling the creation of convincing fake news and propaganda. They can undermine public trust in media and have the potential to influence political elections, stir social unrest, or cause diplomatic tensions.
Legal Considerations: The legal landscape around deepfakes is evolving. Issues like consent, defamation, and intellectual property rights are at the forefront. Some countries and states have started to enact laws specifically targeting malicious deepfake production, but there’s still a long way to go in creating a comprehensive legal framework.
Case Studies: Instances of deepfake misuse, such as manipulated political speeches or fake celebrity videos, have led to public outcry and legal action. Analyzing these cases helps in understanding the real-world implications of deepfakes and shaping appropriate responses.
Preparing for a Deepfake-Prevalent Future
Protection Strategies: Individuals and organizations can protect themselves by staying informed about the nature of deepfakes. Regularly updating cybersecurity measures, using verified sources for information, and being skeptical of implausible content are key strategies.
Media Literacy: Educating the public about media literacy is crucial. This involves teaching people to critically evaluate the content they consume and understand the technology behind media creation, making them less susceptible to deception by deepfakes.
Future Outlook: As deepfake technology becomes more sophisticated, so must our preparedness. This includes continuous development of detection technologies, legal frameworks, and public awareness campaigns. Collaboration between tech companies, governments, and educational institutions will be essential in this endeavor.
Conclusion
Understanding and detecting deepfakes is more important than ever in our digitally driven world. As we stand at the intersection of remarkable technological advancements and ethical challenges, the need for increased awareness and education on this subject cannot be overstated. The journey ahead requires a balanced approach, where innovation is embraced but not at the cost of truth, integrity, and societal well-being. The future of our digital landscape depends on our ability to navigate this complex terrain with informed caution and proactive measures.