Inflammation is a natural process in the body, vital for healing. However, when it becomes chronic, it can lead to various health issues. Recognizing this, expert dietitians have outlined five crucial steps to combat inflammation through dietary changes. These methods focus on both adding beneficial nutrients and avoiding inflammatory triggers.
We consulted Mona Rosene, MS, RD, and Global Director of Scientific Affairs at ChromaDex, for insights into five actionable steps to mitigate inflammation. Rosene emphasizes the importance of diet management, including omega-3s, probiotics, stress control, and Nicotinamide Riboside supplementation as key strategies to reduce inflammation.

Diet plays a pivotal role in managing inflammation. Rosene recommends a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods like herbs, spices, fruits, and vegetables, notably turmeric, berries, tea, and ginger, known for their anti-inflammatory qualities.
These foods deliver essential nutrients and bioactive compounds that combat inflammation through antioxidants and phytochemicals, neutralizing free radicals and regulating inflammatory responses. Simultaneously, limiting intake of inflammation-inducing foods like trans fats, processed items, and alcohol is crucial.
1. Embrace Anti-Inflammatory Foods

Dietitians advise incorporating foods known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Turmeric, berries, green tea, and ginger are not just flavor enhancers; they are packed with antioxidants and phytochemicals that help in fighting inflammation. These nutrients work by neutralizing free radicals and regulating the body’s inflammatory responses.
2. Reduce Inflammatory Food Intake

Just as some foods fight inflammation, others can trigger it. Reducing the intake of trans fats, processed foods, and alcohol is critical. These items contribute to oxidative stress and inflammation, disrupting the body’s balance and exacerbating inflammatory conditions.
3. Increase Omega-3 Fatty Acid Consumption

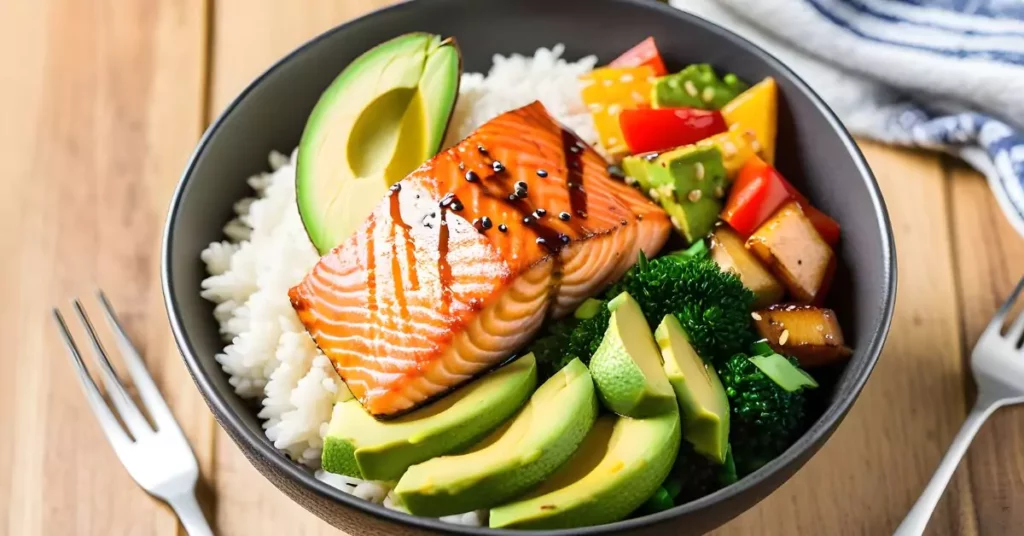
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, flaxseeds, and walnuts, are essential in managing inflammation. These polyunsaturated fats help reduce the body’s inflammatory response by competing with omega-6 fatty acids and positively impacting signaling pathways.
4. Focus on Gut Health with Probiotics

A healthy gut is a cornerstone of overall health, particularly in controlling inflammation. Probiotics, found in fermented foods like yogurt, kombucha, and sauerkraut, support a healthy gut environment, enhancing food digestion and nutrient absorption. This, in turn, maximizes the anti-inflammatory benefits of a well-balanced diet.
5. Manage Stress Effectively

Chronic stress is a significant contributor to inflammation. Engaging in stress management techniques like mindfulness, deep breathing, and regular exercise can regulate stress hormones like cortisol, reducing inflammation.
Conclusion: Integrating Anti-Inflammatory Strategies for Overall Health
In conclusion, Rosene’s recommendations provide a comprehensive approach to fighting inflammation, combining dietary changes, stress management, and supplementation. These steps are not just about reducing inflammation but also about enhancing overall health and well-being.
Adopting these dietitian-recommended steps can lead to significant improvements in managing inflammation. Remember, a well-rounded approach involving diet, stress management, and regular health check-ups is key to maintaining optimal health.